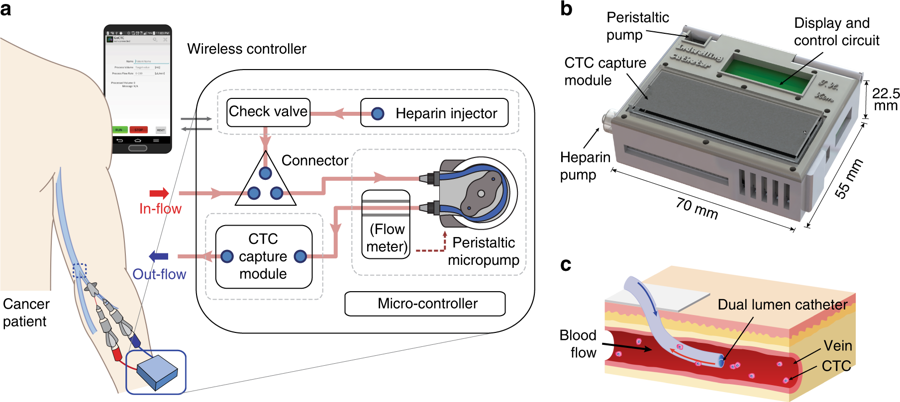
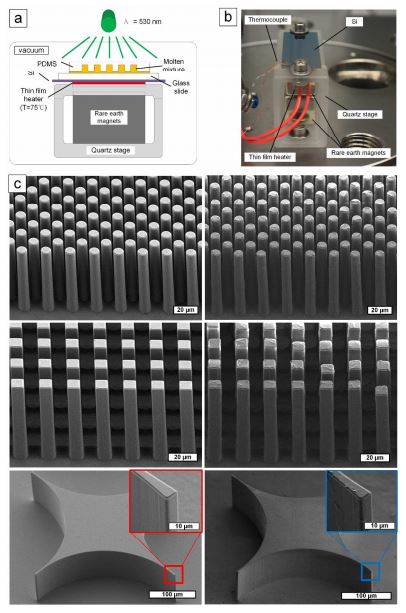
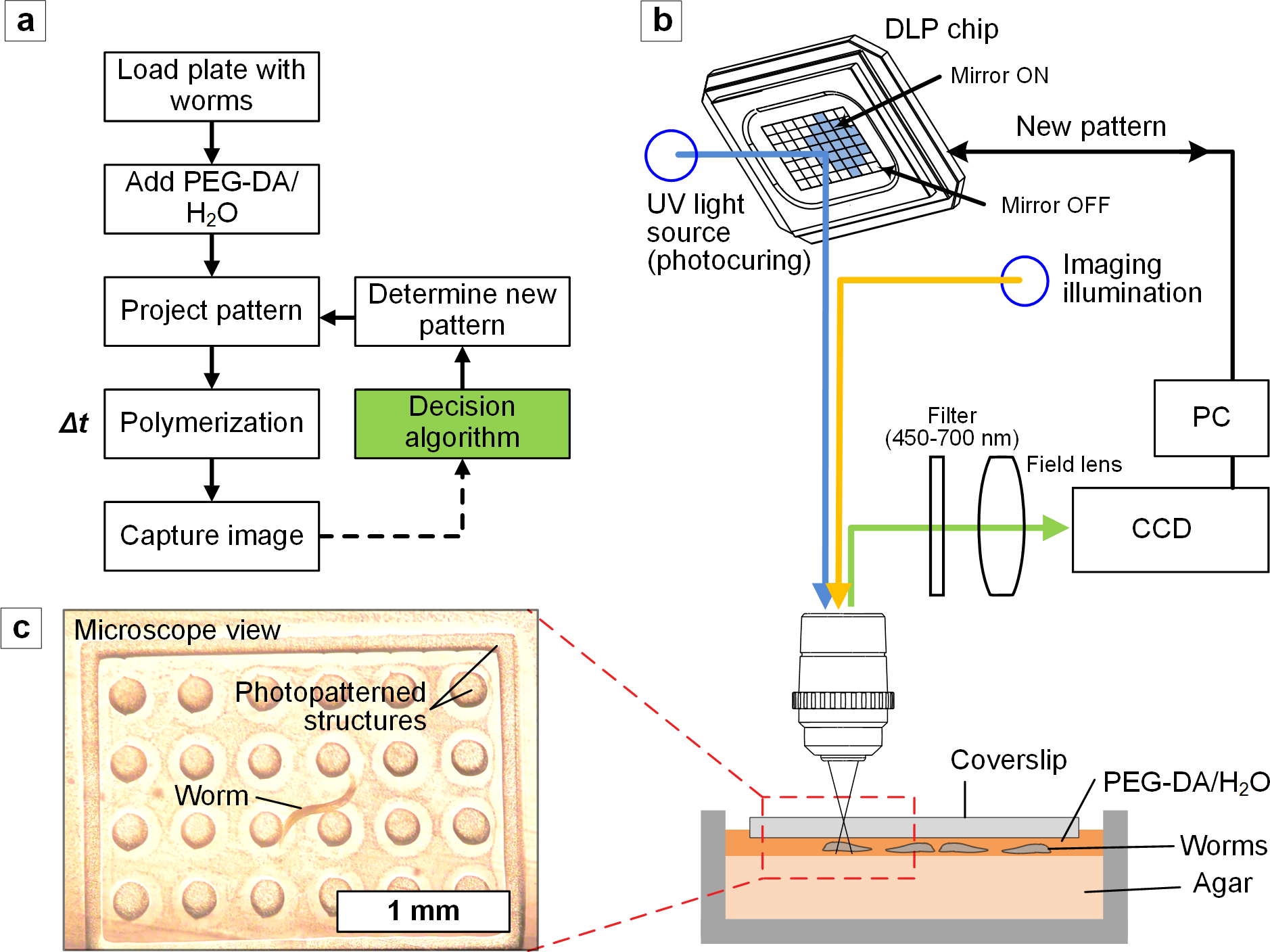
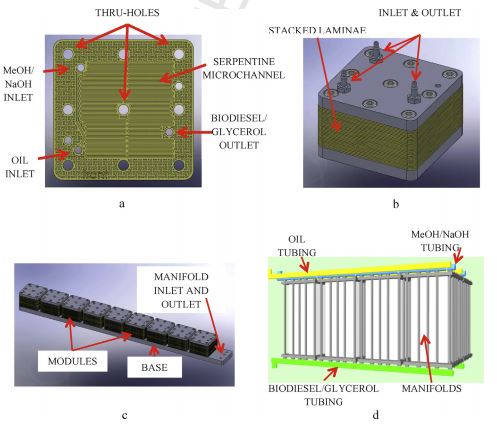
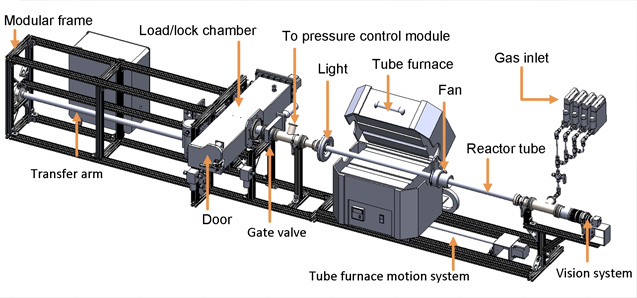
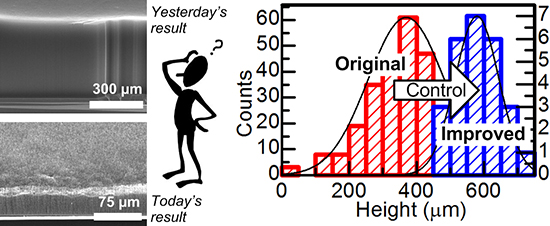
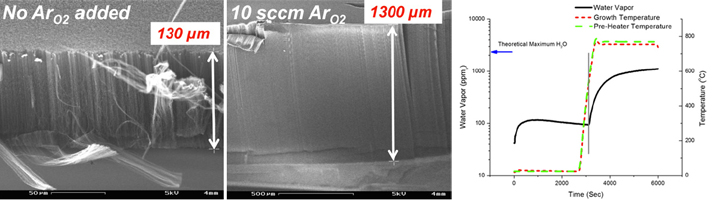
A temporary indwelling intravascular aphaeretic system for in vivo enrichment of circulating tumor cells
Tae Hyun Kim, Yang Wang, C. Ryan Oliver, Douglas H. Thamm, Laura Cooling, Costanza Paoletti, Kaylee J. Smith , Sunitha Nagrath & Daniel F. Hayes. AA temporary indwelling intravascular aphaeretic system for in vivo enrichment of circulating tumor cells. (2019) NATURE COMMUNICATIONS 2019. [DOI: 10.1038/s41467-019-09439-9]
Circulating tumor cells (CTCs) have become an established biomarker for prognosis in patients with various carcinomas. However, current ex vivo CTC isolation technologies rely on small blood volumes from a single venipuncture limiting the number of captured CTCs. This produces statistical variability and inaccurate reflection of tumor cell heterogeneity. Here, we […]